Politics
Debate over independent redistricting commission moves to Senate this year
|
Every ten years, the United States counts its people, tabulating where they live and who they live with, plus a range of factors about them, like their sex, race and ethnicity, age, income, and more.
That census in turn affects people in significant ways, such as the once-a-decade process where local and state governments redraw political district boundaries based on how their population has changed. The goal is to ensure elected officials represent roughly the same amount of people.
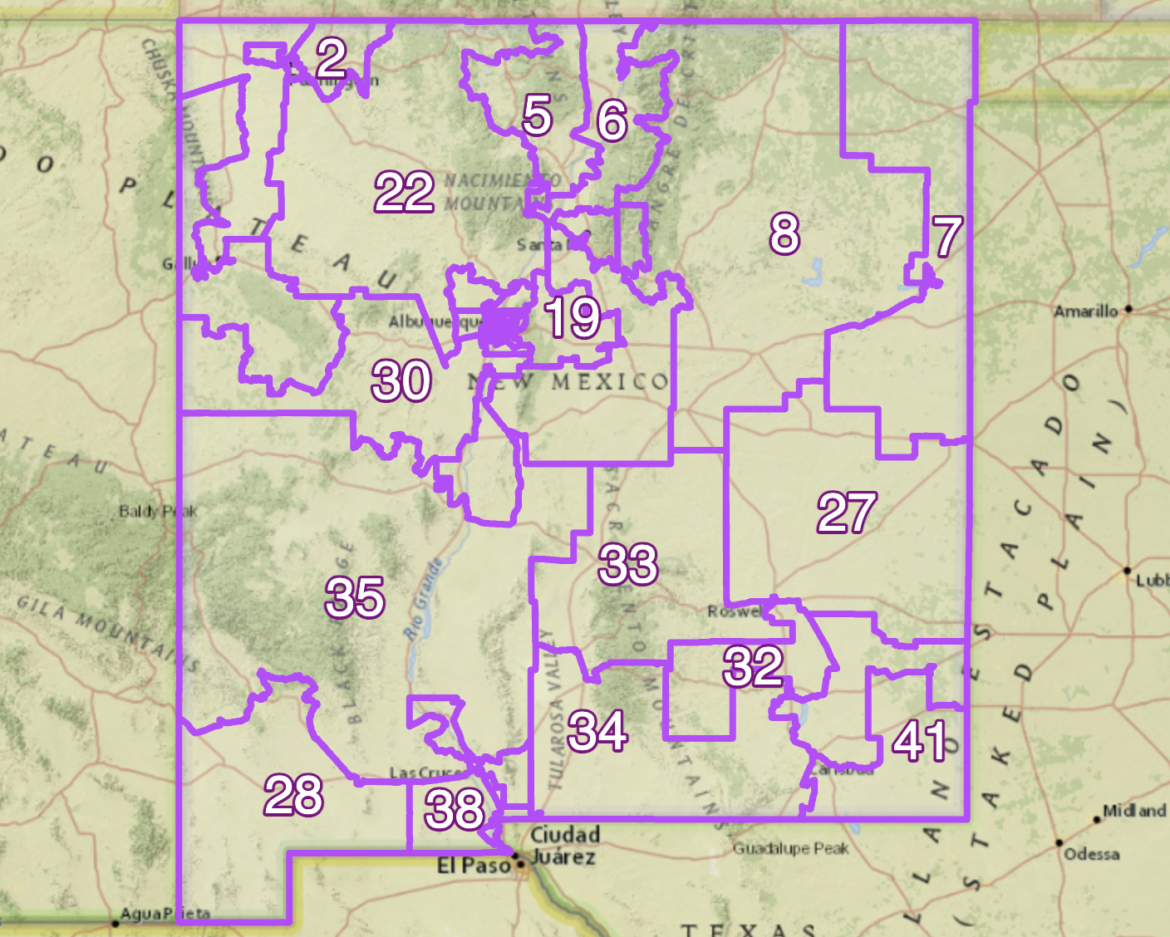
A Senate concept map, one of several the 2021 New Mexico Citizens Redistricting Committee voted to forward to lawmakers for consideration during the official redistricting process. This map-making process is called redistricting, and in New Mexico and most other states, at the state level it’s lawmakers who draw their own political district maps.
But a coalition of advocates and civic groups, and some lawmakers, want voters to decide this November if an independent commission would do a better job than state lawmakers of drawing political districts in the future.
A joint resolution sponsored by Sen. Leo Jaramillo, D-Española, and Sen. Antoinette Sedillo Lopez, D-Albuquerque, would place the idea on the ballot during this fall’s statewide election.
“I heard from New Mexicans from before I won the senate about how they thought a commission should be the one helping decide the district lines to make it fair for every New Mexican and every voting district,” Jaramillo said.
Rep. Natalie Figueroa, who has championed the idea over several years, said there’s “a very direct conflict of interest in the legislators drawing their own boundaries for their own districts.” In order for the public to have faith in democracy, the Albuquerque Democrat said, there needs to be no question that lawmakers might create maps in a way that intentionally protects their own ability to get elected in the future.
In 2019, in a New Mexico In Depth report on redistricting, experts said New Mexico’s redistricting system offered few constraints on how lawmakers choose to draw political district boundaries. After that report was produced, lawmakers created an independent committee to gather input statewide, and then create a series of maps to inform the Legislature’s redistricting process. The Legislature ultimately adopted maps drawn by legislators, and not those recommended by the independent committee.